The IPConfig command is used to view, configure and troubleshoot network-related settings on your computer. It’s commonly used to view the assigned IP Address on a computer, but it can also be used to re-register the DNS records with the ipconfig registerdns command.
You can use the /RegisterDNS parameter to troubleshoot failed DNS registration or to update the DNS records without the need to reboot the computer.
In this article, we will take a look at the IPConfig RegisterDNS command and how to use it.
What is IPConfig /registerdns
The ipconfig /registerdns command updates the DNS server with the current IP address and hostname of the computer that runs the command. It tells the DNS server to create or update a DNS record for that computer so that other computers on the network can find it by its hostname.
When a computer receives a new IP Address from the DHCP server, it will normally also register the DNS record. The computer will also update the DNS record automatically after a reboot or when you leave it on, every 24 hours. But when you change the IP Address manually on the computer, then the DNS record on the server will be incorrect.
Now you could reboot the computer, but another option is to use the IPConfig /RegisterDNS command. This will update or create the DNS records on the server.
How to use IPConfig /registerdns
The IPConfig /registerDNS command can be used in the command prompt, Windows PowerShell and Terminal.
- Right-click on Start and choose Terminal (admin) (or Windows PowerShell (admin))
- Type the command
IPConfig /registerDNSand press enter - Wait for the command to complete
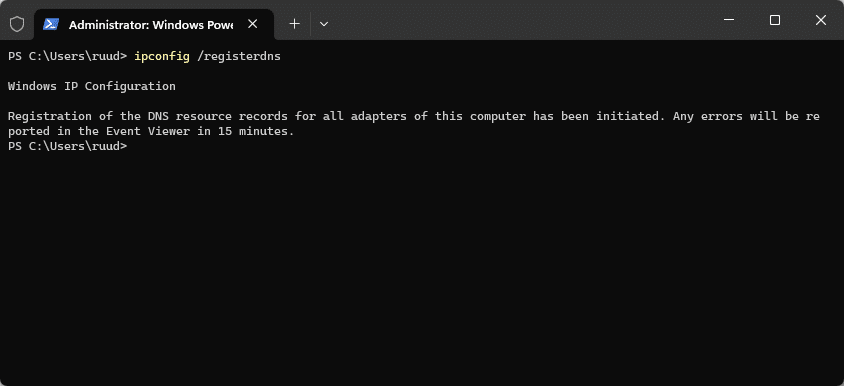
If you want to know if the command was successful, you can either check the DNS server to see if the record is created or updated. Or we can check for any errors in the event viewer.
To view the events, we will first need to enable the DNS Client events log:
- Open the Event Viewer (Windows key + R and type eventvwr)
- Expand Applications and Services Log > Microsoft > Windows
- Open DNS Client Events
- Right-Click on Operational
- Choose Enable Log
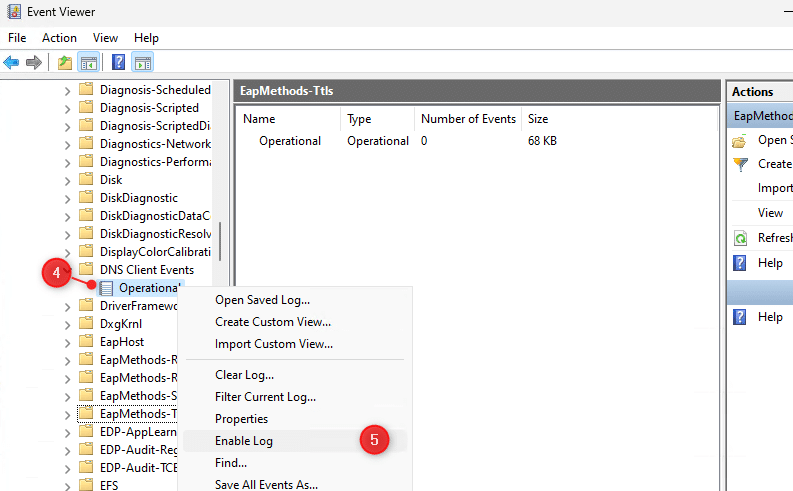
Re-run the command for the logs to get generated. Any errors that might occur will show up in the log.
Automatically Update DNS Record
Your computer will normally update the DNS record automatically. If you are experiencing issues with outdated DNS records, then there are a couple of things you can check.
On the client, open the network adapter:
- Open Start and type Network Connections
- Open View network connections (control panel)
- Double-click on the network adapter
- Click on Properties
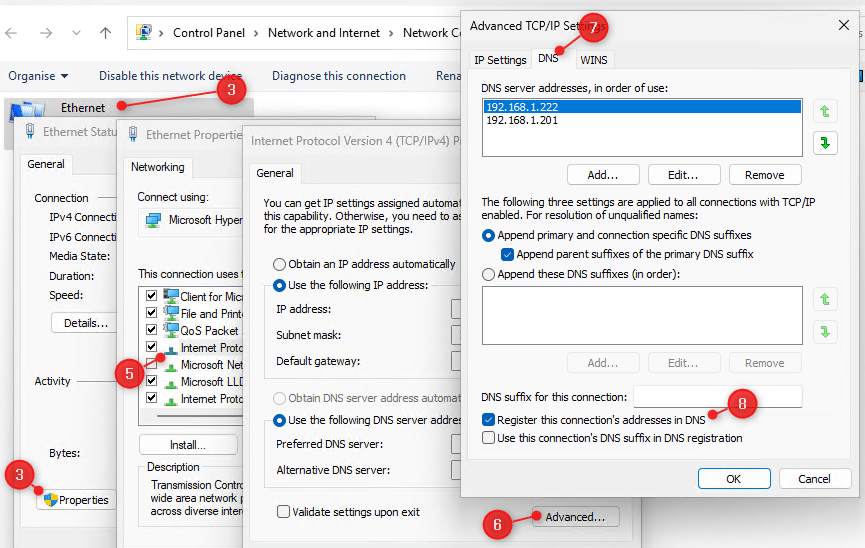
- Double-click on Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)
- Click on Advanced
- Open the DNS tab
- Make sure that Register this connection’s address in DNS is checked.
Another option to check is the DNS Scavenging on your server. By default, old DNS records are not deleted on your DNS server. So make sure that you enable DNS Scavenging and configure DNS Aging correctly.
Wrapping Up
Normally you don’t need to use the ipconfig registerdns command. Windows will take care of registering the DNS automatically. But when you need to troubleshoot DNS-related issues, then the command, combine with the event log, can really help you to find the problem
I hope this article helped you, if you have any questions, then just drop a comment below.




Hi Rudy Mens,
Thanks for your article. But I still have many questions:
1. After running the command, will the timestamp on the DNS server for the A record be updated?
2. After running the command, which event ID on the client indicates the process and results? if there is no error, does it mean re-register successfully? is there any event ID on the server to check if the re-registration was successful?
3. For the DHCP dynamic update, will it monitor the client’s status? for example, if the user switch between WiFi and LAN, will the DHCP server delete the “outdated” IP address(disabled network adaptor’s IP address”). I suspect it can’t delete, because the IP address is still in lease, not expired. So you still have chance that can’t access it, because the laptop was disconnected, but their IP address is still in lease.
4. The laptop will update DNS record every 24 hours, when the timer starts to time and when resets? after reboot, wake up from sleep/hyberate?
Thanks
Best regards