Every network has one, a DHCP Server, but what is it? In short, the DHCP Server assigns a network address (IP Address) to every client in the network that needs one. Without a DHCP server, you would need to give every network device an IP Address manually.
Because of a DHCP server, we can use our mobile phones on every wireless network that we can connect to. The DHCP Server in the network will assign your phone an IP Address so it can connect to the internet for example.
In this article, I am going to explain how a DHCP server works, what it is, and what the optimal settings are.
What is a DHCP Server?
DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol and is a network protocol that is used to assign IP Addresses to clients in a network. Computers, and other network devices, are unable to communicate with each without IP Addresses.
Each network has a DHCP server. In your home network, you will find the DHCP server inside your router. But in a corporate network is an actual server responsible for the DHCP task.
The DHCP server has a pool of IP Addresses that it can lease to a client in the network. The IP Address is only given for a couple of days, after which it’s renewed or given to another client in the network.
Besides IP Addresses, the DHCP also provides the DNS servers and gateway address for the network. Without these, the client would be unable to access the internet.
Why you should use a DHCP Server
An IP Address is basically the digital post address of a network device (computer, printers, etc). If you want to print out your Word document, the computer will send the print job to the IP Address of the printer.
For this to work, the IP Addresses should all be in the same range and unique inside a single network. If two devices have the same IP Address you will get an IP conflict and network packages won’t arrive at the correct destination.
Now you could manually configure IP Addresses on each network client. But that would require you to keep track of which IP Address is used were. And when you connect your notebook for example with the office network, you will need to reconfigure your network setting before you can connect to the internet.
This is where the DHCP server comes in. It allows you to configure a range of IP Addresses that can be assigned to the client in the network. The server keeps track of which device is using which IP Address and makes sure that an IP Address is only used once. This way network clients can easily connect and disconnect from a network without the need to manually configure network settings.
How does a DHCP Server work?
So you now know what a DHCP server is, but how does it work? How does a client (notebook for example) know where to get an IP Address?
When you connect to the (wireless) network, your notebook will send out a broadcast over the network with a DHCP Request. The router will redirect the request to the correct DHCP server (or handle itself, if the router is the DHCP server), which will offer an IP Address to the client.
The process looks like this:
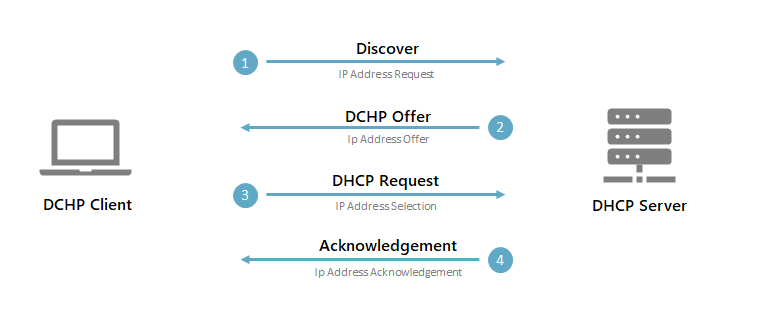
In the DHCP Acknowledgement is the actual IP Address for the client along with other network information. For a client to connect to the internet it will need more than the IP Address alone. It also needs to know which DNS server it can use, what the IP Address is of the router (gateway address), and how long it can use the IP Address (the DHCP Lease time)
So a DHCP Acknowledgement may look like this:
IP Address: 192.168.1.23 Subnetmask: 255.255.255.0 Default gateway: 192.168.1.1 DNS Servers: 1.1.1.1 1.1.0.0 Lease time: 8 days
DHCP Pool
So we have taken a look at how a client gets an IP Address from the Server, but what happens on the DHCP server side?
When settings up your home network you can configure all kinds of settings in the router. One of the settings you can configure is the DHCP Pool. This is a range of IP Addresses that the DHCP server can use to give to network clients.
The default range may reach from 192.168.1.2 to 192.168.1.253, which results in 251 available network addresses. This is a pretty big DHCP pool for a home network or small business. When the DHCP server receives a DHCP Request it will take the first free IP Address from the pool and assign it to the client.
After the DHCP Lease time is passed it will mark the IP Address as available again, so another client can use it.
Tips on settings up your DHCP Server
Configuring the DHCP settings for your home network isn’t difficult. There are only a few settings that you can change in your router, but here are some tips to optimize your network:
DHCP Pool size (DHCP Range)
For home networks you don’t need a large DHCP Pool size, a range from 192.168.1.50 to 192.168.1.199 is more than sufficient. Also for small business networks, this range will work perfectly fine.
I always use the Ip Addresses above 192.168.1.200 for network equipment and the address below 192.168.1.50 for servers.
Static Ip Addresses
Give your network equipment, access points, network printers, etc, a fixed IP Address. This way you can easily connect to them when you need to manage them. Now the downside of a fixed Ip Address is that you may lose track of which IP Address is already in use for which device.
For this, you can use DHCP Reservations. What you basically do is based on the MAC address of a device pre-define which IP Address it should get. You leave the client on DHCP mode, but the server now knows that it always should use the pre-defined IP Address for that particular client.
Lease Time
If you have a small business with a lot of quests on your wireless network, then you want to use a short lease time. But for a home network a business network, a lease time of 8 days is perfectly fine.
If you want to know more about DHCP Lease time, then make sure you check out this article where I explain more about how the DHCP Lease time works and how you can calculate the optimal lease time for your network.
Wrapping Up
I hope that you have now a better understanding of what a DHCP server is and how it works. If you have any questions just drop a comment below.




