#sponsored
A ransomware attack is pretty much the nightmare of every system administrator. Every day new companies become victims of successful ransomware attacks, causing downtime, data, and reputation loss.
To protect our environments, we make off-site backups, beef up the security on our endpoints, and tighten up the firewalls. But did you know that more than 80% of successful ransomware attacks are the result of human error?
Let’s take a look closer look at the role of human error in cybersecurity and how to reduce the chances of human error.
The role of Human Error in Cyber Security Threats
When talking about human error in cybersecurity, most immediately think of users that fall for a phishing mail or download a malware-infected file — basically, something that a user does unintentionally.
However, there is more to it than that. We can divide human error into two categories: skill-based errors and decision-based errors. Unintentional mistakes that lead to a security breach fall into the category of skill-based errors.
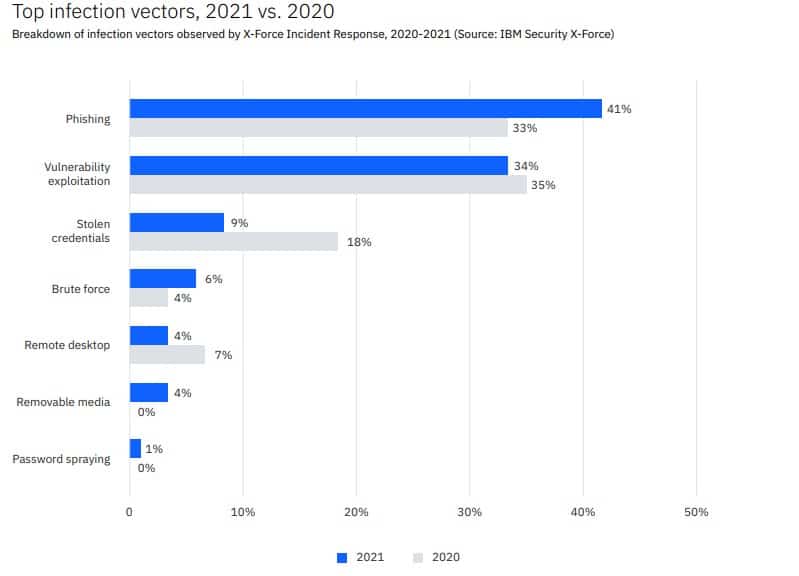
In these cases, the user wasn’t paying attention or wasn’t trained properly. Falling for phishing mail is a great example of a skill-based error. The user either wasn’t trained enough to recognize the phishing mail or was caught off guard and fell for the bait.
With decision-based errors, there is either a lack of action or a lack of knowledge, which results in faulty decisions.
Not keeping your software up to date is a good example of a lack of action. We all know that you need to patch your software and servers in a timely manner. Not keeping them up to date can result in a cybersecurity breach — a result of human error.
Moreover, the lack of knowledge — not understanding the risk of something — is a big threat to cybersecurity. For example, accessing sensitive data over a public wireless network without the use of a VPN. Or writing passwords on a sticky note.
Misdelivery
Another common human error besides skill- and decision-based errors is misdelivery. Misdelivery occurs when a user accidentally sends an email with sensitive information to the wrong person(s). For example, when you hit reply-all, or when you put the recipients in the CC instead of the BCC field.
These kinds of errors don’t result in a ransomware attack, but it still is a cybersecurity breach. Depending on the company and the information leaked, misdelivery can result in dropping stock prices or reputation damage.
Reducing the change of Human Error
So how do we reduce the risk of human error? Well, just like with all security measurements, it’s all about adding layers. Users will keep making mistakes if they don’t know what the risks are or how to handle certain situations. Thus, we need to reduce the possibility of human errors as much as possible. Below are some ways to do so.
Using Policies and Controls
The first step to ensuring cybersecurity robustness and reducing human error is to implement the right policies and controls in your organization. For example, not all users need to have access to personal or sensitive data. If a user can’t access it, then they also can’t share it by accident.
Data loss prevention (DLP) policies in Microsoft 365, for example, scan outgoing documents and emails for sensitive data such as social security numbers or credit card numbers. It can trigger an alert or send an email for approval to a manager before it’s sent out. This extra set of eyes reduces the chance of unintentionally sharing sensitive information.
Password policies and MFA
Credentials being stolen via phishing emails is still the most common type of data breach. The problem is that they often take a long time to identify — more than 300 days on average — and cost an average of $4.5 million dollar per data breach [2].
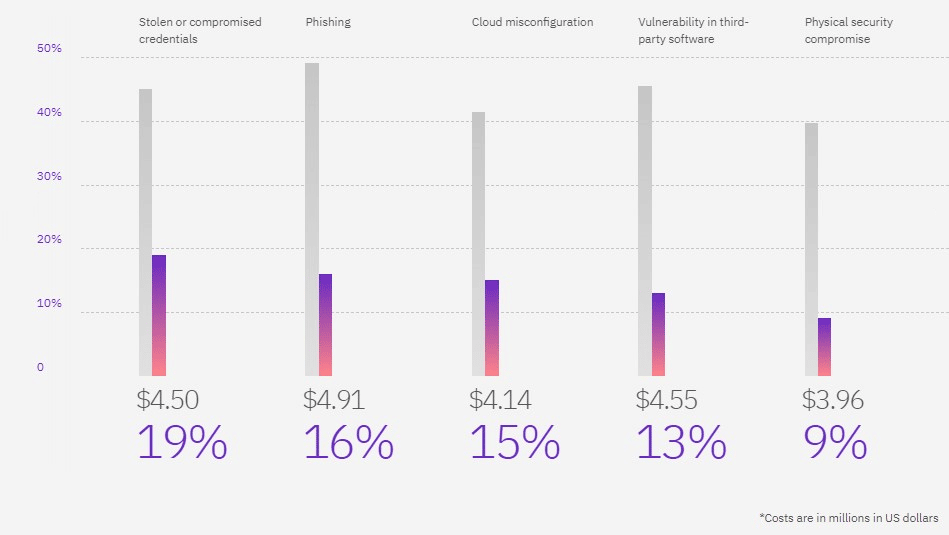
Strong and unique passwords are, of course, the first step — but they are also a problem. Users find it hard to remember them and often write them down on sticky notes. Implementing features like Windows Hello for Business can make it less of a burden for your users. Likewise, giving your users access to a password manager reduces the chance of reusing passwords and the sticky note problem.
The next step in securing your user’s credentials is the use of multi-factor authentication (MFA). If it’s available, then you should use it — full stop. And that should also be the official company policy. MFA is, these days, luckily mandatory on Microsoft 365.
The only problem that we see with MFA is “MFA fatigue”. Users get the push notification too often, resulting in them blindly accepting the requests. I actually experienced this last year in one of the tenants that I manage. The user in question fell victim to a phishing attack a couple of days earlier, and at the moment of the MFA request, he wasn’t even working on his computer. Still, he approved the MFA request, which resulted in a data breach.
To counteract MFA fatigue, we can do a couple of things. We can reduce the amount of MFA requests for trusted devices to 90 days, for example. This helps to prevent users from unintentionally approving the MFA request.
Another important feature to add is number matching. . This way, users can approve a request only by matching the number that is displayed on the login screen. And of course, the last step is user training. Make sure that they know which actions can result in an MFA request, as well as what to do when they get a request without login action.
Make it discussible
A common problem in organizations is that users are afraid to tell when they did something wrong. This is often not limited to cybersecurity only, but it’s a big part of the problem.
When users are more forthcoming about mistakes they have made, then the impact of the incident can often be greatly reduced. And this isn’t limited to just users; IT staff must also be open and transparent about mistakes that they make. Only together can you reduce cybersecurity risks and limit the impact of breaches.
User Awareness Training
Even with all the possible security measures, humans are still the weakest link. This is why user awareness training is so important. They need to be able to recognize phishing, impersonations emails, and other cyber security threats.
Awareness training isn’t limited to phishing emails only. Data protection, securely working from a remote location, passwords, and general IT hygiene should also be addressed.
When it comes to user awareness training, it’s important to repeat the basics regularly. A single hour-long session isn’t going to be effective; users will forget it after a couple of weeks. Good user awareness training needs to be interactive and tailored to the users’ needs because some users require more training than others.
Wrapping Up
It’s evident that we need to reduce the chances of human error when it comes to cybersecurity breaches, given the big part human error plays in successful ransomware attacks.
We can reduce the opportunities with the help of the right security measurements and tools. But more important is that we invest in our users, and train them with tailored user awareness training programs. Only this way can we make a big impact on the human error risk in cybersecurity.
sources:
– [1] IBM X-Force Threat Intelligence Index 2022
– [2] https://www.ibm.com/reports/data-breach